How much compression should a chainsaw have?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on chainsaw engine compression and its importance for optimal performance. As seasoned chainsaw experts with over two decades of hands-on experience, we understand the intricacies of engine compression and its impact on your chainsaw’s efficiency and longevity. In this article, we will explore the ideal compression range, the significance of engine compression, troubleshooting techniques, and essential maintenance practices. Let’s dive right in!
What is Chainsaw Engine Compression?
In the world of chainsaws, engine compression refers to the pressure created during the compression stroke of the combustion cycle. Modern chainsaws typically utilize two-stroke engines, which complete one full combustion cycle with just two piston movements or strokes.
During the compression stroke, the air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber as the piston moves upward, effectively compressing this mixture. Subsequently, in the combustion stroke, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, leading to a powerful explosion that drives the piston downward, generating the necessary power to operate the chainsaw.
Impact of Engine Compression on Different Chainsaw Applications
Forestry: In forestry, chainsaws with optimal engine compression are essential for felling trees efficiently and safely. High compression ensures the saw can handle the demanding work without frequent stalling or loss of power.
Landscaping: For landscaping tasks such as pruning and trimming, chainsaws with proper compression provide smooth operation and precise cuts, making the work easier and more efficient.
Home Use: Home users rely on chainsaws for various tasks, from cutting firewood to clearing fallen branches. Ensuring good engine compression helps maintain the tool’s reliability and longevity, reducing maintenance frequency and costs.
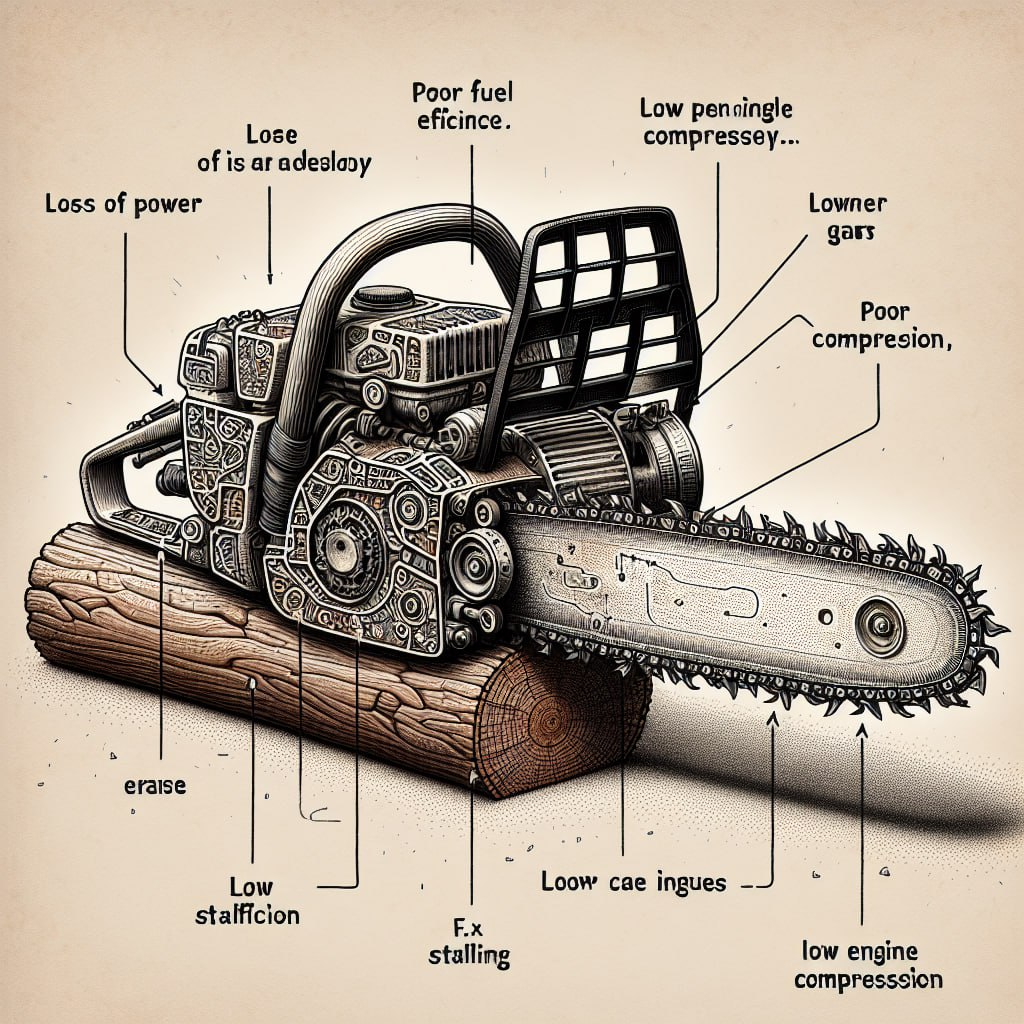
Consequences of Low Compression
Insufficient compression, commonly referred to as low compression, can lead to various detrimental effects on your chainsaw’s performance. Let’s explore some of the key issues associated with low compression:
- Loss of Power: Inadequate compression results in less powerful explosions within the combustion chamber, leading to a noticeable loss of power during operation.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: With lower pressure in the combustion chamber, the fuel does not burn effectively. As a result, unburnt fuel and exhaust gases escape, causing poor fuel efficiency and unnecessary wastage.
- Struggles to Start: Chainsaws with compression levels below 110 psi often face difficulties starting. Even if the engine starts, it may not sustain operation for an extended period, and power output will be significantly reduced.
- Stalling: Low compression can cause frequent stalling, particularly when operating the chainsaw under load. The insufficiently compressed air-fuel mixture fails to ignite properly, making it challenging for the engine to remain running consistently.
Risks of High Compression
While low compression is a more common issue, it’s important to mention the risks associated with high compression as well. Excessive compression, defined as compression levels above 160 psi, can lead to problems such as pre-ignition and knocking. These issues not only affect the chainsaw’s performance but also pose a risk of severe damage to the engine.
READ ALSO: [Solved] 13 Reasons Why Stihl Chainsaw Won’t Start, Troubleshooting, Starting Problem
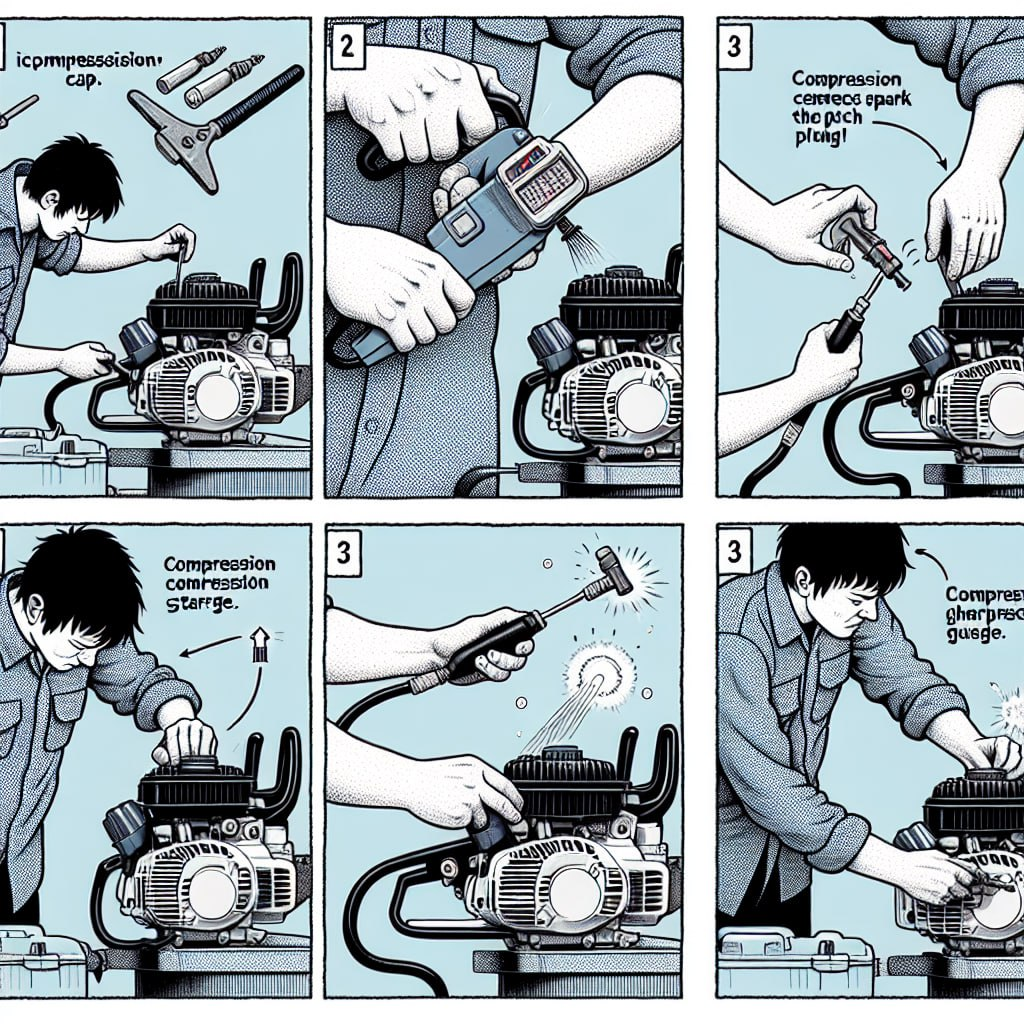
Testing Chainsaw Engine Compression
To ensure your chainsaw is operating at optimal compression levels, periodic testing is crucial. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you accurately test your chainsaw’s engine compression:
- Preparation: Remove the back cover of your saw and disconnect the spark plug using a scrench (screwdriver/wrench combination tool).
- Compression Tester Setup: Attach the compression tester’s adapter securely into the spark plug hole. Ensure it is snug but avoid over-tightening. Zero the gauge on the tester.
- Wide-Open Throttle: Hold the throttle wide open during the compression test. You can use zip ties to maintain the throttle in the fully open position.
- Pull the Starter Cord: Pull the starter cord multiple times, around 5-6 pulls, until the needle on the compression tester gauge stops moving.
- Record the Reading: Once the needle stabilizes, take note of the PSI reading displayed on the gauge.
Case Studies and Examples
Case Study 1: Forestry Application
A professional logger experienced frequent stalling and poor fuel efficiency with their chainsaw. Compression testing revealed a reading of 90 psi, indicating low compression. Upon inspection, worn piston rings were identified as the cause. Replacing the piston rings restored the chainsaw’s performance, allowing the logger to resume work efficiently.
Case Study 2: Home Use
A homeowner struggled to start their chainsaw, which also exhibited low power output. Testing showed a compression of 100 psi. The issue was traced to a leaky head gasket, which was promptly replaced. This repair improved the chainsaw’s starting reliability and power.
Common Symptoms of Compression Problems
- Unusual Noises: Clicking or knocking sounds during operation can indicate compression issues.
- Smoke: Excessive smoke from the exhaust may signal improper fuel combustion due to low compression.
- Overheating: High engine temperatures can result from poor compression and inefficient combustion.
Troubleshooting Low Compression
If your chainsaw exhibits signs of low compression, it is essential to identify the underlying cause and address it promptly. Here are the top 6 reasons for low engine compression:
- Worn Piston Rings: Over time, piston rings can wear down, resulting in decreased sealing capability. This wear leads to a loss of compression and is a common cause of low compression.
- Cylinder Wall Damage: Similar to piston rings, the cylinder walls may also experience wear over time, reducing compression. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to identify and rectify this issue.
- Leaky Head Gasket: A damaged head gasket is unable to seal the combustion chamber effectively, resulting in loss of compression. If identified, the head gasket should be promptly repaired or replaced.
- Worn or Damaged Valves: Worn intake or exhaust valves fail to seal properly, leading to compression loss. Regular valve maintenance and inspection can prevent this issue from occurring.
- Wrong Valve Timing: Incorrect valve timing significantly impacts compression levels, as the valves may fail to open and close at the appropriate intervals. Ensuring proper valve timing is crucial for optimal compression.
- Carbon Deposits: Excessive carbon buildup on the piston crown, valves, or cylinder head can hinder proper compression. Regular cleaning and inspection help prevent the accumulation of carbon deposits.
When troubleshooting low compression, it is advisable to inspect and potentially replace piston rings and the head gasket. Additionally, regular cylinder checks are essential for maintaining optimal compression levels.

Maintenance Checklist
- Monthly Checks: Inspect piston rings, cylinder walls, and valves for signs of wear.
- Lubrication: Ensure proper lubrication according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Fuel Quality: Use high-quality fuel and oil to prevent carbon deposits.
- Annual Compression Test: Perform a compression test annually or when performance issues arise.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule professional maintenance for comprehensive diagnostics and repairs.
FAQs
What is the ideal compression for a chainsaw?
The ideal compression for most chainsaws is between 110 and 160 psi.
How often should I test my chainsaw’s compression?
It’s recommended to test your chainsaw’s compression at least once a year or if you notice any performance issues.
Can I use regular engine oil in my chainsaw?
No, it’s best to use the specific two-stroke oil recommended by the manufacturer for optimal performance.
What are the signs of high compression in a chainsaw?
High compression can cause pre-ignition, knocking, and excessive engine wear.

Wrapping Up
In conclusion, chainsaw engine compression plays a pivotal role in determining the performance and reliability of your equipment. By understanding the importance of optimal compression levels, conducting regular testing, and addressing issues promptly, you can ensure that your chainsaw operates at its best.
